Book Value Per Common Share BVPS: Definition and Calculation
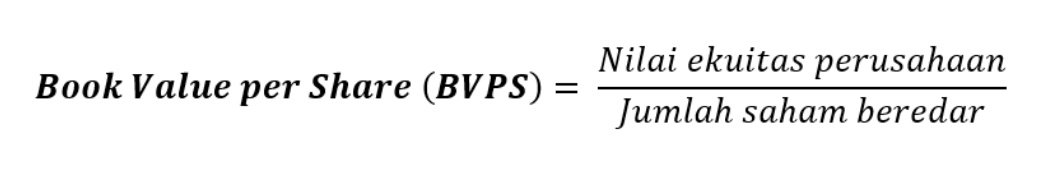
This differs from the book value for investors because it is only used internally for managerial accounting purposes. If the book value per share is higher than its market value per share then it can indicate an undervalued stock. If the book value per share is lower than its market value per share, it can indicate an overpriced, or overvalued stock. This sometimes creates problems for companies with assets that have greatly appreciated; these assets cannot be re-priced and added to the overall value of the company. There are other factors that you need to take into consideration before making an investment.
Methods to Increase the Book Value Per Share
Note that if the company has a minority interest component, the correct value is lower. Minority interest is the ownership of less than 50 percent of a subsidiary’s equity by an investor or a company other than the parent company. Investors can find a company’s financial information in quarterly and annual reports on its investor relations page. However, it is often easier to get the information by going to a ticker, such as AAPL, and scrolling down to the fundamental data section. InvestingPro offers detailed insights into companies’ Book Value Per Share including sector benchmarks and competitor analysis.
Increase Assets and Reduce Liabilities
Failing bankruptcy, other investors would ideally see that the book value was worth more than the stock and also buy in, pushing the price up to match the book value. The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books. The following image shows Coca-Cola’s “Equity Attributable to Shareowners” line at the bottom of its Shareowners’ Equity section. In this case, that total of $24.1 billion would be the book value of Coca-Cola. It’s one metric that an investor may look for if they’re interested in valuating Coca-Cola as a potential investment.
Book Value vs. Market Value: What’s the Difference?
On the other hand, investors and traders are more interested in buying or selling a stock at a fair price. When used together, market value and book value can help investors determine whether a stock is fairly valued, overvalued, or undervalued. While market cap represents the market perception of a company’s valuation, it may not necessarily represent the real picture. It is common to see even large-cap stocks moving 3 to 5 percent up or down during a day’s session. Stocks often become overbought or oversold on a short-term basis, according to technical analysis. Book value does not always include the full impact of claims on assets and the costs of selling them.
Market Value

This reduces the stock’s outstanding shares and decreases the amount by which the total stockholders’ equity is divided. For example, in the above example, Company X could repurchase 500,000 shares to reduce its outstanding shares from 3,000,000 to 2,500,000. They evaluate it with several other metrics, including price-to-earnings ratio, free cash flow trends, debt-to-equity ratio, and payout ratio for dividend stocks.
Market Value Formula
That could happen if it always uses straight-line depreciation as a matter of policy. When we divide book value by the number of outstanding shares, we get the book value per share (BVPS). Outstanding shares consist of all the company’s stock currently held by all its shareholders. That includes share blocks held by institutional investors and restricted shares. For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns. U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require marketing costs to be expensed immediately, reducing the book value per share.
That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company. In some cases, a company will use excess earnings to update equipment rather than pay out dividends or expand operations. Manufacturing companies offer a good example of how depreciation can affect book value. These companies have to pay huge amounts of money for their equipment, but the resale value for equipment usually goes down faster than a company is required to depreciate it under accounting rules.
- Relying solely on market value may not be the best method to assess a stock’s potential.
- Enterprise value, or firm value, market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one another for contrast.
- Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock is trading below or above its intrinsic value.
- Market value—also known as market cap—is calculated by multiplying a company’s outstanding shares by its current market price.
- The Bottom Line Using book value is one way to help establish an opinion on common stock value.
Book value is the amount found by totaling a company’s tangible assets (such as stocks, bonds, inventory, manufacturing equipment, real estate, and so forth) and subtracting its liabilities. In theory, book value should include everything down to the pencils and staples used by employees, but for simplicity’s sake, companies generally only franked dividend definition include large assets that are easily quantified. Others include the debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio, earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and the working capital ratio. Although investors have many metrics for determining the valuation of a company’s stock, two of the most commonly used are book value and market value.
Tangible book value is the same thing as book value except it excludes the value of intangible assets. Intangible assets have value, just not in the same way that tangible assets do; you cannot easily liquidate them. By calculating tangible book value we might get a step closer to the baseline value of the company. It’s also a useful measure to compare a company with a lot of goodwill on the balance sheet to one without goodwill. There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment.
Physical assets, such as inventory, property, plant, and equipment, are also part of total assets. Intangible assets, including brand names and intellectual property, can be part of total assets if they appear on financial statements. Total liabilities include items like debt obligations, accounts payable, and deferred taxes. For example, Walmart’s January 31, 2012 balance sheet indicates that shareholders’ equity has a value of $71.3 billion. The number is clearly stated as a subtotal in the equity section of the balance sheet.
